The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loan program is a mortgage loan initiative offered by the United States government to aid individuals, particularly first-time homebuyers, in achieving homeownership. The distinguishing feature of FHA loans is their federal government backing, which mitigates risk for lenders and facilitates qualification for borrowers with lower credit scores or limited down payments. FHA loans typically necessitate a down payment as low as 3.5% of the home’s purchase price, rendering them accessible to a wider range of buyers. Furthermore, FHA loans offer competitive interest rates and more flexible qualification criteria, rendering them a popular choice for those who may not meet the rigorous requirements of conventional loans. However, borrowers are obligated to pay mortgage insurance premiums to safeguard the lender in the event of default, which constitutes an additional cost associated with these loans.
Eligibility Criteria
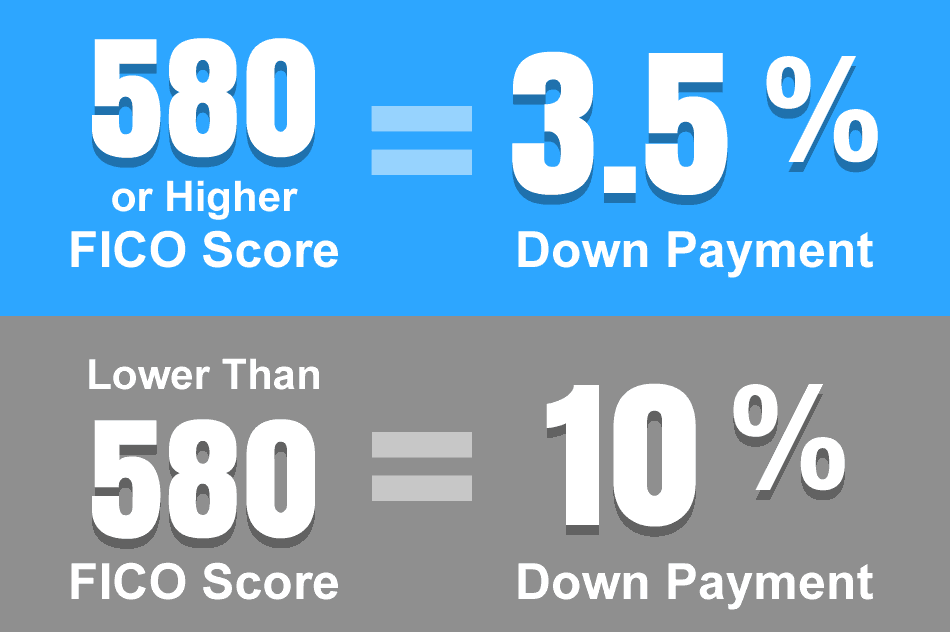
The eligibility criteria for FHA loans have been designed to facilitate homeownership for a diverse range of borrowers. In order to be eligible for an FHA loan, applicants are typically required to possess a minimum credit score, which may vary but is generally around 580 or higher. While lower credit scores may be considered, they may necessitate a larger down payment. Furthermore, borrowers must possess a stable employment history and adequate income to cover the mortgage payments. Eligibility is also extended to U.S. citizens and legal residents. One of the most notable features of FHA loans is the relatively low down payment requirement, which can often be as low as 3.5% of the home’s purchase price, rendering them an attractive option for first-time buyers. Fulfilling these eligibility criteria provides access to this government-backed mortgage program, which offers a pathway to homeownership for individuals who may not qualify for conventional loans due to more stringent requirements.
FHA Loan Credit Score Criteria: https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.fha.com%2Ffha_article%3Fid%3D210&psig=AOvVaw1pu3lGGcO56As4W4FdZXKQ&ust=1696437881630000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CBAQjRxqFwoTCMDJnNyp2oEDFQAAAAAdAAAAABAE
Benefits and Drawbacks
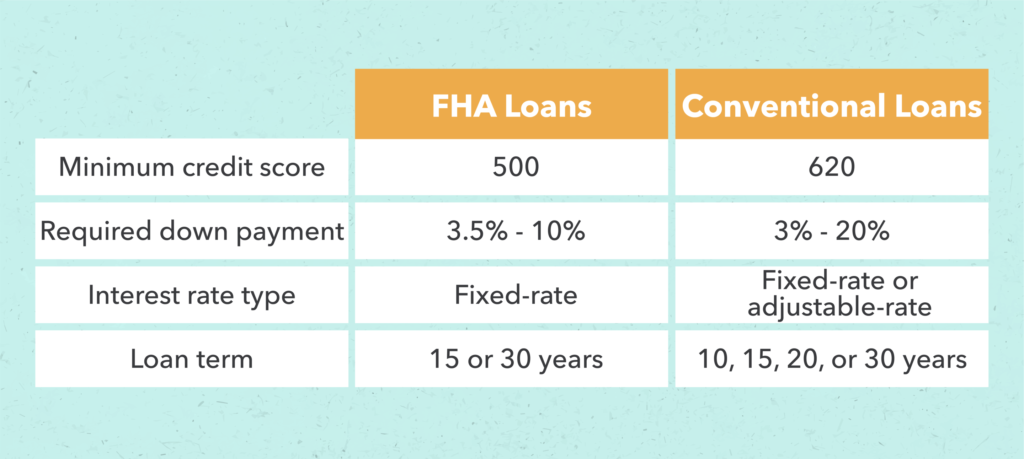
FHA loans present a set of advantages and disadvantages that borrowers must carefully evaluate when selecting their mortgage options. One of the primary benefits is the low down payment requirement, which enables buyers to acquire a property with as little as 3.5% down, thereby enhancing the feasibility of homeownership, particularly for first-time buyers. Additionally, FHA loans offer more flexible credit requirements, accommodating borrowers with lower credit scores. However, there are also drawbacks to consider. Borrowers are obligated to pay upfront and annual mortgage insurance premiums, which augment the overall cost of the loan. Moreover, FHA loan limits may restrict financing options in high-cost areas. While FHA loans provide accessibility, they may not always be the most cost-effective choice in the long run, and borrowers should weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks when making their decision.
FHA Loans vs. Conventional Loans Breakdown: https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fmint.intuit.com%2Fblog%2Fhousing%2Ffha-loan-requirements-573%2F&psig=AOvVaw19nux7E3ksGWraTqKzSugK&ust=1696437547931000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CBAQjRxqFwoTCMjJkr2o2oEDFQAAAAAdAAAAABAJ
Application Process
The process of applying for an FHA loan involves a series of essential steps that borrowers must undertake to secure their mortgage. Initially, applicants must identify an FHA-approved lender to collaborate with, as only these lenders are authorized to originate FHA loans. The process commences with a pre-approval, where borrowers furnish financial information to determine their eligibility and potential loan amount. Once pre-approved, borrowers can commence their search for a suitable home within the FHA loan limits for their area. After identifying a suitable property, an appraisal is conducted to evaluate its value and ensure it meets FHA standards. Concurrently, applicants submit a formal loan application, providing comprehensive financial documentation such as income, employment history, and credit information. The lender reviews the application and gathers the necessary paperwork. If approved, the loan proceeds to underwriting, where it is meticulously evaluated for compliance with FHA guidelines. Finally, upon approval, borrowers can close on the loan, sign the necessary documents, and secure their FHA-backed mortgage. It is imperative to comprehend and efficiently navigate this process for a successful FHA loan application.
FHA Loan Application Types: https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.fha.com%2Ffha_article%3Fid%3D2881&psig=AOvVaw3Hsulje6gi1Lrnq4rvXiX4&ust=1696437773464000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CBAQjRxqFwoTCLCe2aip2oEDFQAAAAAdAAAAABAE
The consideration of FHA loan limits and types is of great importance for prospective borrowers. FHA loan limits serve as a restriction on the maximum amount of mortgage that the Federal Housing Administration will insure in a particular region, and these limits vary based on the differences in housing costs across locations. Borrowers who intend to purchase homes that exceed these limits may need to explore alternative financing options, such as conventional loans. With regard to FHA loan types, the standard FHA loan, commonly known as the 203(b)(link to more details about this loan) loan, is the most prevalent and is intended for the acquisition or refinancing of a primary residence. Additionally, there are specialized FHA loan programs, such as the 203(k) loan, which provides financing for both the purchase of a home and necessary renovations or repairs. Familiarizing oneself with the loan limits in their area and the various FHA loan types available can enable borrowers to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate mortgage option for their specific needs and circumstances.




